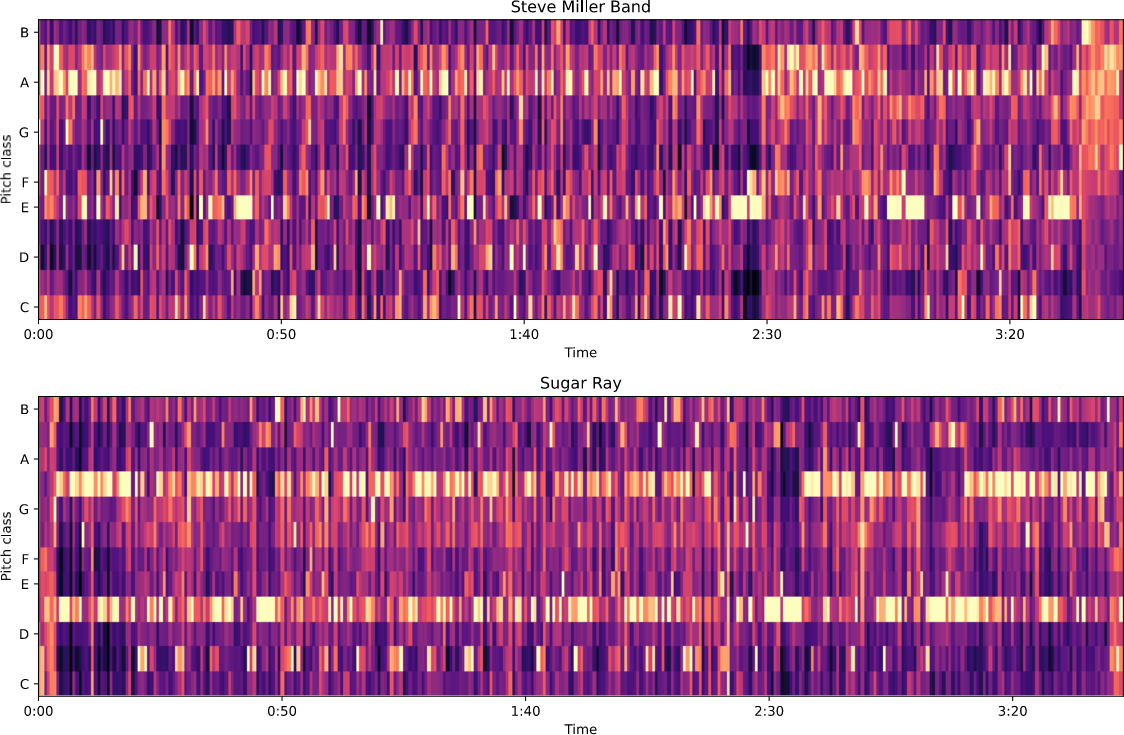
y1, sr = librosa.load("smooth.mp3")
hop = 512
chroma = librosa.feature.chroma_cqt(y=y1, hop_length=hop)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 3))
img = librosa.display.specshow(chroma, hop_length=hop, y_axis='chroma', x_axis='time', ax=plt.gca())
plt.title("Smooth Criminal: Michael Jackson")
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Smooth Criminal: Michael Jackson')